手写 LRU
题目
用 JS 实现一个 LRU 缓存
LRU 使用
Least Recently Used 最近最少使用
即淘汰掉最近最少使用的数据,只保留最近经常使用的资源。它是一个固定容量的缓存容器。
js
const lruCache = new LRUCache(2); // 最大缓存长度 2
lruCache.set(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lruCache.set(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lruCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lruCache.set(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lruCache.get(2); // 返回 null
lruCache.set(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lruCache.get(1); // 返回 null
lruCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lruCache.get(4); // 返回 4分析
- 哈希表,即
{ k1: v1, k2: v2, ... }形式。可以O(1)事件复杂度存取keyvalue - 有序。可以根据最近使用情况清理缓存
JS 内置的数据结构类型 Object Array Set Map ,恰好 Map 符合这两条要求
Map 是有序的
Map 有序,Object 无序
实现
代码参考 LRU.ts
ts
export default class LRUCache {
private length: number
private data: Map<any, any> = new Map()
constructor(length: number) {
if (length < 1) throw new Error('invalid length')
this.length = length
}
set(key: any, value: any) {
const data = this.data
if (data.has(key)) {
data.delete(key)
}
data.set(key, value)
if (data.size > this.length) {
// 如果超出了容量,则删除 Map 最老的元素
const delKey = data.keys().next().value
data.delete(delKey)
}
}
get(key: any): any {
const data = this.data
if (!data.has(key)) return null
const value = data.get(key)
data.delete(key)
data.set(key, value)
return value
}
}
// const lruCache = new LRUCache(2)
// lruCache.set(1, 1) // {1=1}
// lruCache.set(2, 2) // {1=1, 2=2}
// console.info(lruCache.get(1)) // 1 {2=2, 1=1}
// lruCache.set(3, 3) // {1=1, 3=3}
// console.info(lruCache.get(2)) // null
// lruCache.set(4, 4) // {3=3, 4=4}
// console.info(lruCache.get(1)) // null
// console.info(lruCache.get(3)) // 3 {4=4, 3=3}
// console.info(lruCache.get(4)) // 4 {3=3, 4=4}注意,get set 时都要把操作数据移动到 Map 最新的位置。
扩展
实际项目中可以使用第三方 lib
- https://www.npmjs.com/package/quick-lru
- https://www.npmjs.com/package/lru-cache
- https://www.npmjs.com/package/tiny-lru
- https://www.npmjs.com/package/mnemonist
连环问:不用 Map 如何实现 LRU cache ?
LRU cache 是很早就有的算法,而 Map 仅仅是这几年才加入的 ES 语法。
使用 Object 和 Array
根据上文的分析,两个条件
- 哈希表,可以用
Object实现 - 有序,可以用
Array实现
js
// 执行 lru.set('a', 1) lru.set('b', 2) lru.set('c', 3) 后的数据
const obj1 = { value: 1, key: 'a' }
const obj2 = { value: 2, key: 'b' }
const obj3 = { value: 3, key: 'c' }
const data = [obj1, obj2, obj3]
const map = { 'a': obj1, 'b': obj2, 'c': obj3 }模拟 get set 操作,会发现几个问题,都来自于数组
- 超出 cache 容量时,要移除最早的元素,数组
shift效率低 - 每次
getset时都要把当前元素移动到最新的位置,数组splice效率低
Array 改为双向链表
数组有问题,就需要使用新的数据结构 双向链表
ts
Interface INode {
value: any
next?: INode
prev?: INode
}双向链表可以快速移动元素。末尾新增元素 D 很简单,开头删除 A 元素也很简单。
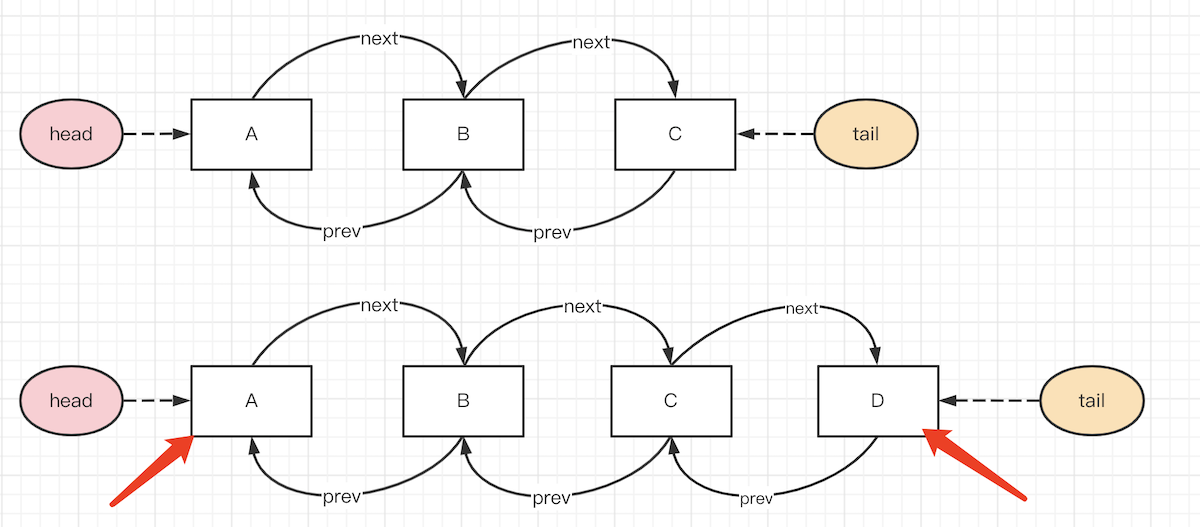
要把中间的元素 B 移动到最后(如 LRU set get 时移动数据位置),只需要修改前后的指针即可,效率很高。
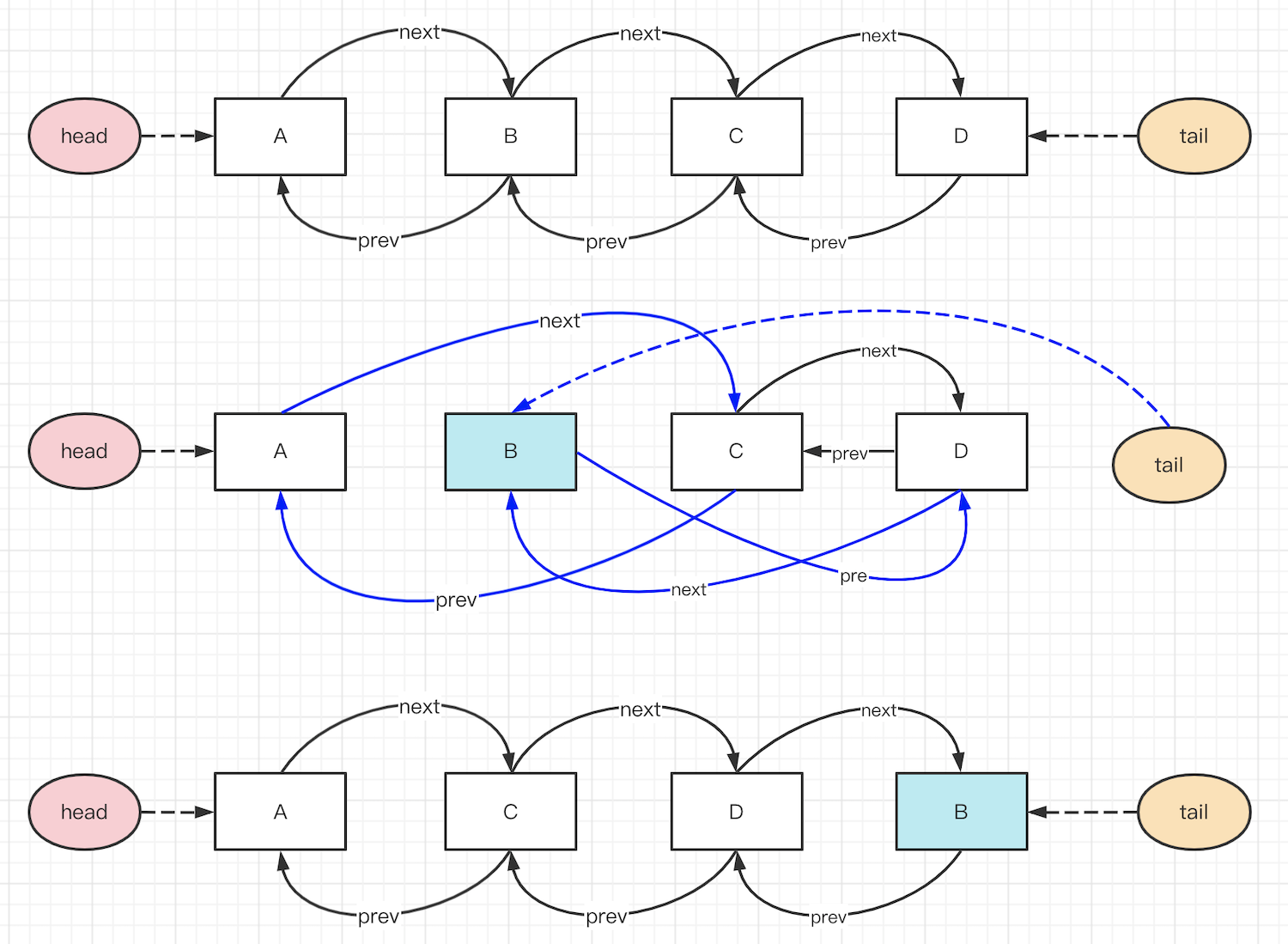
实现
代码参考 LRU2.ts
ts
interface IListNode {
value: any
key: string // 存储 key ,方便删除(否则删除时就需要遍历 this.data )
prev?: IListNode
next?: IListNode
}
export default class LRUCache {
private length: number
private data: { [key: string]: IListNode } = {}
private dataLength: number = 0
private listHead: IListNode | null = null
private listTail: IListNode | null = null
constructor(length: number) {
if (length < 1) throw new Error('invalid length')
this.length = length
}
private moveToTail(curNode: IListNode) {
const tail = this.listTail
if (tail === curNode) return
// -------------- 1. 让 prevNode nextNode 断绝与 curNode 的关系 --------------
const prevNode = curNode.prev
const nextNode = curNode.next
if (prevNode) {
if (nextNode) {
prevNode.next = nextNode
} else {
delete prevNode.next
}
}
if (nextNode) {
if (prevNode) {
nextNode.prev = prevNode
} else {
delete nextNode.prev
}
if (this.listHead === curNode) this.listHead = nextNode
}
// -------------- 2. 让 curNode 断绝与 prevNode nextNode 的关系 --------------
delete curNode.prev
delete curNode.next
// -------------- 3. 在 list 末尾重新建立 curNode 的新关系 --------------
if (tail) {
tail.next = curNode
curNode.prev = tail
}
this.listTail = curNode
}
private tryClean() {
while (this.dataLength > this.length) {
const head = this.listHead
if (head == null) throw new Error('head is null')
const headNext = head.next
if (headNext == null) throw new Error('headNext is null')
// 1. 断绝 head 和 next 的关系
delete headNext.prev
delete head.next
// 2. 重新赋值 listHead
this.listHead = headNext
// 3. 清理 data ,重新计数
delete this.data[head.key]
this.dataLength = this.dataLength - 1
}
}
get(key: string): any {
const data = this.data
const curNode = data[key]
if (curNode == null) return null
if (this.listTail === curNode) {
// 本身在末尾(最新鲜的位置),直接返回 value
return curNode.value
}
// curNode 移动到末尾
this.moveToTail(curNode)
return curNode.value
}
set(key: string, value: any) {
const data = this.data
const curNode = data[key]
if (curNode == null) {
// 新增数据
const newNode: IListNode = { key, value }
// 移动到末尾
this.moveToTail(newNode)
data[key] = newNode
this.dataLength++
if (this.dataLength === 1) this.listHead = newNode
} else {
// 修改现有数据
curNode.value = value
// 移动到末尾
this.moveToTail(curNode)
}
// 尝试清理长度
this.tryClean()
}
}
// const lruCache = new LRUCache(2)
// lruCache.set('1', 1) // {1=1}
// lruCache.set('2', 2) // {1=1, 2=2}
// console.info(lruCache.get('1')) // 1 {2=2, 1=1}
// lruCache.set('3', 3) // {1=1, 3=3}
// console.info(lruCache.get('2')) // null
// lruCache.set('4', 4) // {3=3, 4=4}
// console.info(lruCache.get('1')) // null
// console.info(lruCache.get('3')) // 3 {4=4, 3=3}
// console.info(lruCache.get('4')) // 4 {3=3, 4=4}注意事项
- 数据结构如何定义,
data和链表分别存储什么 - 双向链表的操作(非常繁琐,写代码很容易出错,逻辑一定要清晰!!!)
- 链表
node中要存储data.key,否则删除data需要遍历、效率低